Antonio Pigafetta's account of the Magellan-Elcano voyage gives us both first-hand historical detail and color—the human aspects of the journey.
The Italian scholar learned all he could about the cultures that Magellan's fleet encountered, even sitting down and recording samples of languages.
An excellent example of Pigafetta's curiosity and fascination is his description of the coconut and the palm tree, which he learned about soon after the fleet's arrival in the Philippines. Like the pineapple Magellan tried in Rio, the coconut was an unknown.
"Cocoanuts are the fruit of the palmtree. Just as we have bread, wine, oil, and milk, so those people get everything from that tree.
"They get wine in the following manner. They bore a hole into the heart of the said palm at the top called palmito [i.e., stalk], from which distils a liquor which resembles white must. That liquor is sweet but somewhat tart, and [is gathered] in canes [of bamboo] as thick as the leg and thicker. They fasten the bamboo to the tree at evening for the morning, and in the morning for the evening.
"That palm bears a fruit, namely, the cocoanut, which is as large as the head or thereabouts. Its outside husk is green and thicker than two fingers. Certain filaments are found in that husk, whence is made cord for binding together their boats.
"Under that husk there is a hard shell, much thicker than the shell of the walnut, which they burn and make therefrom a powder that is useful to them.
"Under that shell there is a white marrowy substance one finger in thickness, which they eat fresh with meat and fish as we do bread; and it has a taste resembling the almond. It could be dried and made into bread.
"There is a clear, sweet water in the middle of that marrowy substance which is very refreshing. When that water stands for a while after having been collected, it congeals and becomes like an apple.
"When the natives wish to make oil, they take that cocoanut, and allow the marrowy substance and the water to putrefy. Then they boil it and it becomes oil like butter.
"When they wish to make vinegar, they allow only the water to putrefy, and then place it in the sun, and a vinegar results like [that made from] white wine.
[107]"Milk can also be made from it for we made some. We scraped that marrowy substance and then mixed the scrapings with its own water which we strained through a cloth, and so obtained milk like goat’s milk.
"Those palms resemble date-palms, but although not smooth they are less knotty than the latter.
"A family of ten persons can be supported on two trees, by utilizing them week about for the wine; for if they did otherwise, the trees would dry up. They last a century."
Image: Agnieszka Kwiecień, Nova, CC BY-SA 3.0. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0.
(C) 2021 by John Sailors. All rights reserved.
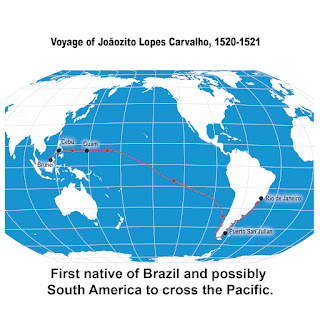
Ferdinand Magellan’s historic journey swept up several unlikely travelers along the way, among them a seven-year-old boy at Guanabara Bay (Rio de Janeiro). Half-Portuguese, half-Tupi Indian, he is remembered in history as Joãozito Lopes Carvalho. The young boy became the first native of Brazil and likely all of South America to cross the Pacific Ocean—on a year-and-a-half journey that for him ended at Brunei five hundred years ago this summer.
Antonio Pigafetta's account of the Magellan-Elcano voyage gives us both first-hand historical detail and color—the human aspects of the journey. The Italian scholar learned all he could about the cultures that Magellan's fleet encountered, even sitting down and recording samples of languages.
An excellent example of Pigafetta's curiosity and fascination is his description of the coconut and the palm tree, which he learned about soon after the fleet's arrival in the Philippines. Like the pineapple Magellan tried in Rio, the coconut was an unknown. "Cocoanuts are the fruit of the palmtree. Just as we have bread, wine, oil, and milk, so those people get everything from that tree. Read more.
A handful of medieval travelogues were the closest thing Ferdinand Magellan had to a travel guide when he sought a westward route to Asia—accounts credited to Marco Polo, John Mandeville, and others, and those all echoed the same monsters and myths repeated since the time of Pliny the Elder, the Roman author whose Naturalis Historiae helped inspire the encyclopedia.
It gets little mention today, but The Travels of Sir John Mandeville was a world atlas of sorts in medieval Europe, essential reading for navigators and explorers. The accounts became circulated widely in Europe in the fourteenth century. They detail travels in North Africa and the Middle East, and in India, China, and even the Malay Peninsula—which would have been of particular interest to Ferdinand Magellan, and also Enrique of Malacca, Magellan’s interpreter-slave. Read more.
Reni Roxas and Marc Singer brought the story of Enrique to life for children in First Around the Globe: The Story of Enrique. Twenty years on they released this anniversary edition in 2017 from Tahanan Books, Manila. Read more.
On March 16, 1521, Magellan and his crew reached the Philippines, where they would finally be able to recover after three months crossing the Pacific. They were unable to stop long at Guam—their encounter with the Chamorros they met there did not go well, as seen in their sendoff. As they were departing, more than a hundred of the Chamorros’ outrigger canoes followed for more than a league.
- EnriqueOfMalacca.com
- Enrique of Malacca on Twitter
- Enrique of Malacca on Facebook
- John Sailors / Enrique on Medium
- And, yes, Enrique might be 500 years old, but he was known as a kid, so of course he's now on Instagram too.